Statistical controversies in clinical research: limitations of open-label studies assessing antiangiogenic therapies with regard to evaluation of vascular adverse drug events—a meta-analysis - Annals of Oncology
![PDF] Bias was reduced in an open-label trial through the removal of subjective elements from the outcome definition. | Semantic Scholar PDF] Bias was reduced in an open-label trial through the removal of subjective elements from the outcome definition. | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/814ad6ccbfa9defca4d2b00c4672f9070cf6b8da/16-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Bias was reduced in an open-label trial through the removal of subjective elements from the outcome definition. | Semantic Scholar
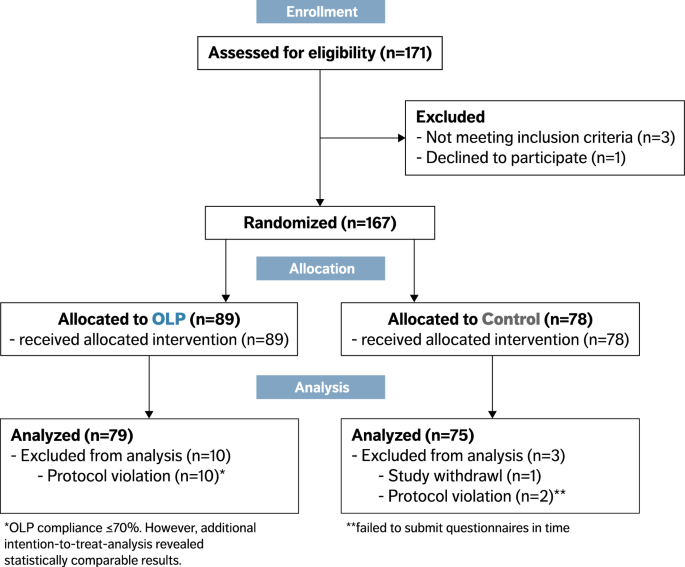
Effects of open-label placebos on test performance and psychological well-being in healthy medical students: a randomized controlled trial | Scientific Reports

Bias was reduced in an open-label trial through the removal of subjective elements from the outcome definition - Journal of Clinical Epidemiology

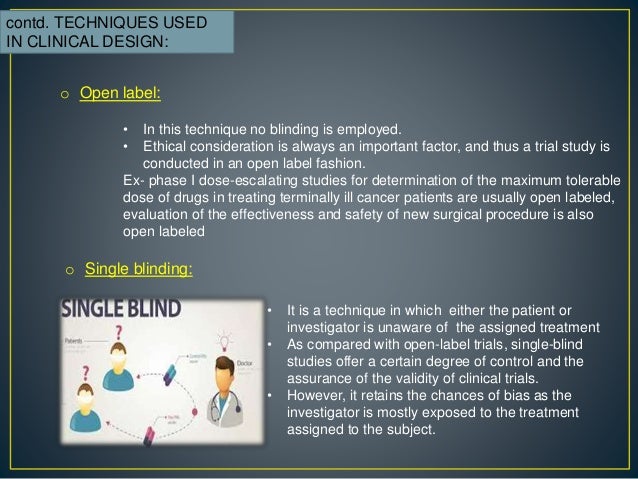
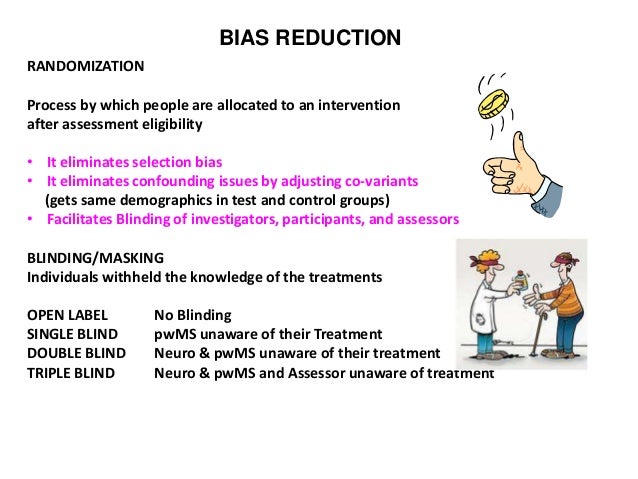
Epidemiology Clinical Trials Outline Basic principles Biases Ethics- GCP Statistical analysis Ethics. - ppt download
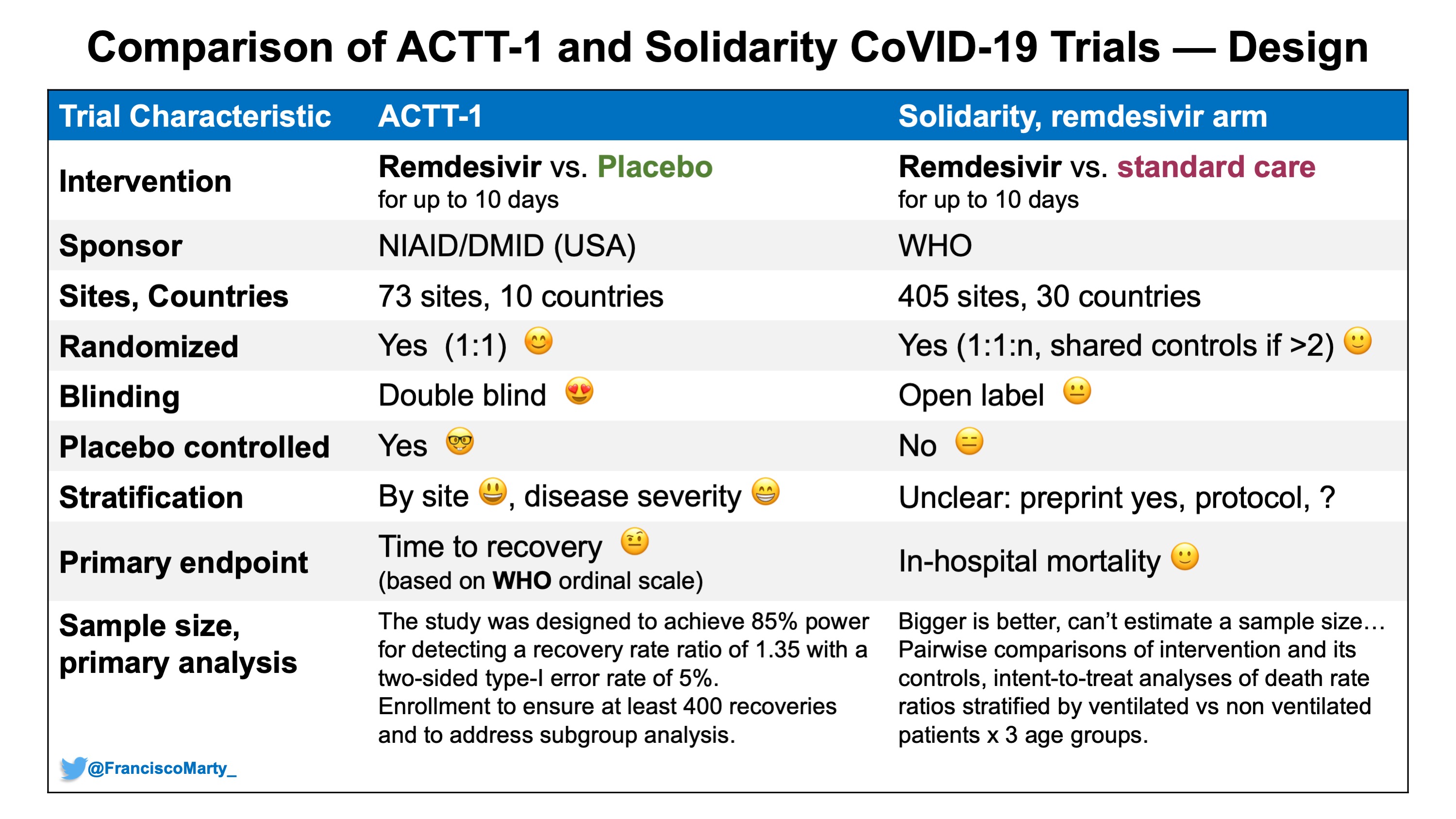
Francisco Marty, MD on Twitter: "Here is a first table comparing some basic design characteristics between #ACTT1 and #SolidarityTrial - major difference the open-label design in Solidarity vs. concealed allocation and double-blind

Statistical controversies in clinical research: limitations of open-label studies assessing antiangiogenic therapies with regard to evaluation of vascular adverse drug events—a meta-analysis - Annals of Oncology

PDF) Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome assessment is not feasible: Strategies from two randomised trials

Design characteristics, risk of bias, and reporting of randomised controlled trials supporting approvals of cancer drugs by European Medicines Agency, 2014-16: cross sectional analysis | The BMJ

Design characteristics, risk of bias, and reporting of randomised controlled trials supporting approvals of cancer drugs by European Medicines Agency, 2014-16: cross sectional analysis | The BMJ

Design characteristics, risk of bias, and reporting of randomised controlled trials supporting approvals of cancer drugs by European Medicines Agency, 2014-16: cross sectional analysis | The BMJ